QR code variants
Model 1
Model 1 QR code is an older version of the specification. It is visually similar to the widely seen model 2 codes, but lacks alignment patterns. Differences are in the bottom right corner, and in the midsections of the bottom and right edges are additional functional regions.

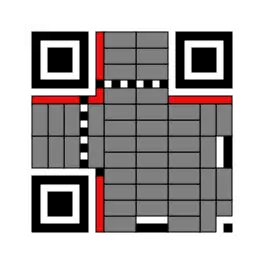
Micro QR code
Micro QR code is a smaller version of the QR code standard for applications where symbol size is limited. There are four different versions (sizes) of Micro QR codes: the smallest is 11×11 modules; the largest can hold 35 numeric characters.

IQR code
IQR Code is an alternative to existing QR codes developed by Denso Wave. IQR codes can be created in square or rectangular formations; this is intended for situations where a rectangular barcode would otherwise be more appropriate, such as cylindrical objects. IQR codes can fit the same amount of information in 30% less space. There are 61 versions of square IQR codes, and 15 versions of rectangular codes. For squares, the minimum size is 9 × 9 modules; rectangles have a minimum of 19 × 5 modules. IQR codes add error correction level S, which allows for 50% error correction. IQR Codes have not yet been given an ISO/IEC specification, and only proprietary Denso Wave products can create or read IQR codes.
Secure QR code
Secure Quick Response (SQR) code is a QR code that contains a "private data" segment after the terminator instead of the specified filler bytes "ec 11". This private data segment must be deciphered with an encryption key. This can be used to store private information and to manage company's internal information.
SQR codes have been developed by the FORUS Foundation to enable secure transactions, and published under a Creative Commons Licence. The SQR solution guarantees the integrity of the source data as well as the validity of the originating party. The payment instruction string is made up of the electronic instruction data from the scanned QR code appended with a SHA-2 cryptographic hash. The message digest can then be encrypted using the private key of the sender, which then creates a digital signature of the message. This signature validates the integrity of the data and the trustworthiness of the sender. This provides non-repudiation, confirming the identity of the sender, and that it has not been tampered with during transmission. By embedding the URL and all the variables required to perform shopping cart type e-commerce, bill payment and peer to peer payments, coupled with a digital certificate eliminates the possibility of spoofing, tampering, and man in the middle attacks.
Frame QR
Frame QR is a QR code with a "canvas area" that can be flexibly used. In the center of this code is the canvas area, where graphics, letters, and more can be flexibly arranged, making it possible to lay out the code without losing the design of illustrations, photos, etc.
HCC2D
Researchers have proposed a new High Capacity Colored 2-Dimensional (HCC2D) Code, which builds upon a QR code basis for preserving the QR robustness to distortions and uses colors for increasing data density (as of 2014 it is still in prototyping phase). The HCC2D code specification is described in details in Querini et al. (2014), while techniques for color classification of HCC2D code cells are described in detail in Querini and Italiano (2014), which is an extended version of Querini and Italiano (2013).
Introducing colors into QR codes requires addressing additional issues. In particular, during QR code reading only the brightness information is taken into account, while HCC2D codes have to cope with chromatic distortions during the decoding phase. In order to ensure adaptation to chromatic distortions which arise in each scanned code, HCC2D codes make use of an additional field: the Color Palette Pattern. This is because color cells of a Color Palette Pattern are supposed to be distorted in the same way as color cells of the Encoding Region. Replicated color palettes are used for training machine learning classifiers.
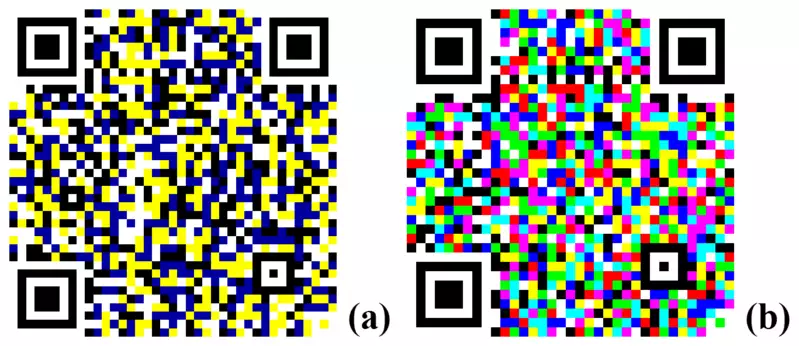
JAB code
JAB code (Just Another Barcode) is a color 2D matrix symbology made of color squares arranged in either square or rectangle grids. It was developed by Fraunhofer Institute SIT (Secure Information Technology).
The code contains one primary symbol and optionally multiple secondary symbols. The primary symbol contains four finder patterns located at the corners of the symbol.
The code uses either 4 or 8 colours. The 4 basic colours (cyan, magenta, yellow, black) are the 4 primary colours of the subtractive CMYK color model which is the most widely used system in industry for colour printing on a white base such as paper. The other 4 colours (blue, red, green, white) are secondary colours of the CMYK model and originate as an equal mixture of a pair of basic colours.
The barcode is not subject to licensing and was submitted to ISO/IEC standardization as ISO/IEC 23634 expected to be approved at the beginning of 2021 and finalized in 2022. The software is open-source and published under the LGPL v2.1 license. The specification is freely available.
Because the colour adds a third dimension to the two-dimensional matrix, a JAB code can contain more information in the same area compared to two-colour (black and white) codes – theoretically twice as much data for a 4 colour code and three times more for 8 colours assuming the same encoding algorithm. This can allow storage of an entire message in the barcode, rather than just storing partial data with a reference to a full message somewhere else (such as a link to a website), thus eliminating the need for additional always-available infrastructure beyond the printed barcode itself. It may be used to digitally sign encrypted digital version of printed legal documents, contracts and certificates (diplomas, training), medical prescriptions or provide product authenticity assurance to increase protection against counterfeits.

Source: Wikipedia.com
More information

 Sign in
Sign in